Overview Of Azure Blue Prints
In a commercial environment, repeatedly deploying the same Azure resources can cause stress. Furthermore, human resources are inefficient in repeating the same work with greater efficiency. The one-stop solution for this problem is to combine all of these resources into a single Azure service. It is now feasible with Azure Blueprints. Azure Blueprints generates a complete set of Azure resources.
This blog post will teach you about Azure Blueprints, what they are used for, and how they may help you deploy resources in the Azure environment. By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of how to construct and publish Azure Blueprints.
Azure Blueprints Overview:
Architects use the word "blueprints" to develop and build new things. They are mostly employed to ensure that the final design meets specifications and is built in accordance with the organization's standards and requirements.
Azure Blueprints is a Microsoft Azure service that works in the same way as traditional blueprints. It is used by a security architect or engineer to design and develop software according to specifications. The repeating collection of Azure resources can be built and deployed using the Azure Blueprints' predefined requirements and standards.
IT workers can use the Azure Blueprints to create an ARM template as well as Azure artifacts including role assignments, resource groups, and policy assignments. The Azure Cosmos DB database, which is globally distributed, handles the backend service. Regardless of where the items are placed in the Azure Blueprints, they can be duplicated across several Azure regions to provide highly availability and low latency access to those things.
What are the artifacts available in the Azure Blueprints?
The Azure blueprint objects used are listed below:
• Role Assignments: This feature allows the user to add a user, role, access, etc.
• Policy Assignments: You can add either an inbuilt Azure policy or a bespoke policy.
• Azure Resource Manager Templates: You can add an ARM template.
• Resource Groups: You can create a resource group.
Azure Blueprint Lifecycle
Azure blueprints have their own natural lifecycle. The blueprints offered in Azure can be produced and deployed. They can be erased when they are no longer required. It also offers continuous integration and deployment for enterprises that leverage infrastructure as code.
The major stages of the Azure Blueprint lifecycle include:
• Blueprint Creation
• Blueprint Publication
• Version Management
• Version Publication
• Version Deletion
• Blueprint deletion
How to create Azure Blueprints?
Here, I have listed the steps on how to create Azure Blueprint:
1. Begin by logging into the Azure portal.
2. In the Azure Portal, go to "All Services," then "Management followed by Governance," and finally "Blueprints.
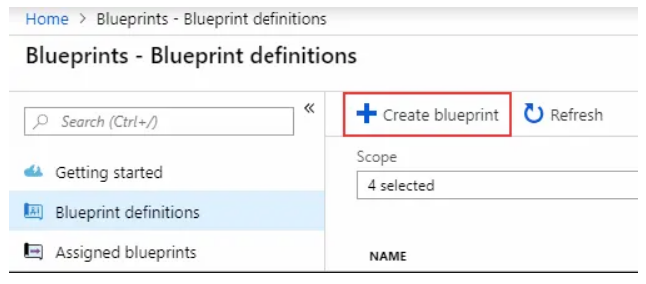
1. On the subsequent screen, select the "Create" button.
2. On the "Create blueprint" tab, select "Start with a blank blueprint.".
3. Under the "Basics" tab, give the new blueprint a name. Next, open the scope selector by clicking the ellipsis button next to the "Definition location" field. Choose the subscription you want and click "Select." Once the subscription has been selected, click "Next: Artifacts."
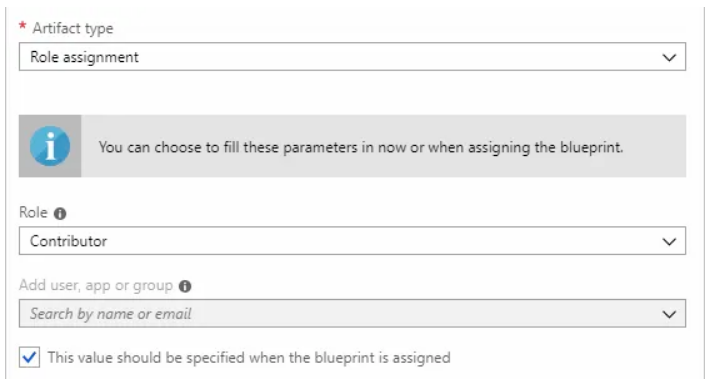
1. The "Artifacts" page displays an empty list because no artifacts have yet been added. To add one, go to the "Subscription" section and click "Add artifact". On the following screen, enter the "Artifact type" dropdown menu and pick "Resource group," then click "Add."
2. Next, in the "Resource group" section, click "Add artifact" and select "Contributor role" from the "Role" dropdown.
3. Finally, to generate the blueprint, select "Save Draft." This action will save the blueprint as a draft, and it will appear in your blueprint definitions.
How to publish Azure Blueprints?
1. From the list of blueprint definitions, select the draft blueprint that was previously saved while creating the blueprint.
2. Next, select the Publish blueprint option to begin the publishing process.
3. Select the version and key in the description in the change notes box, then click the publish button.
4. After publishing the blueprint, you will be able to view the newly updated version.
Azure Blueprints vs. Resource Manager Templates
Understanding the fundamental differences between Azure Blueprints and Azure Resource Manager templates is critical for determining which can be utilized and when. First, let's define Azure Blueprints.
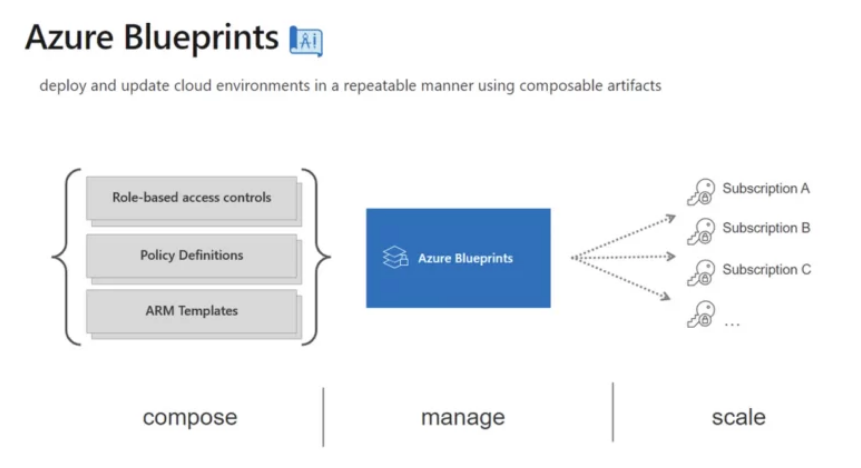
Azure Blueprints can be used to configure the environment, including Azure resource groups, various policies, role assignments, and Resource Manager template deployments. It includes the Essential packages, which allow you to integrate all of your resources and artifacts in one place. These packages can be created, allocated, and versioned to the appropriate subscriptions. They are also audited and tracked for their activities.
Azure Blueprints can help to bridge the gap between blueprint components and deployed apps. The ARM template has no active link with the deployed application. This type of connection can help with monitoring and auditing Azure resources.
Furthermore, while the ARM template is not natively available in Azure, the Azure blueprint can be replicated in several regions.
Azure Blueprints vs. Azure Policy
As we've already contrasted Azure Blueprints and ARM Templates, we need to look at what Azure Policy is.
An Azure policy functions as a control mechanism, granting default rights while specifically prohibiting access to certain properties of both new and existing resources to which the policy applies. An Azure Blueprint, on the other hand, is a bundle that defines precise criteria and requirements for Azure service deployment, as well as security measures and design concepts. These packages are intended for reuse, encouraging consistency and adherence to compliance standards across all resources.
When a policy is included in a blueprint, it acts as a method for establishing the appropriate architectural patterns or designs when the blueprint resources in Azure are assigned. Furthermore, policy inclusions ensure that any changes made to the resources or environment to which the blueprint is allocated are consistent with approved changes, ensuring ongoing compliance with the blueprint's criteria.
Benefits of using Azure Blueprints
The Azure Blueprints features and benefits are as follows:
Create and deploy compliant networks
Azure Blueprints can deploy large-scale Azure resources with a comprehensive set of artifacts, such as Azure Resource Manager templates, role-based access controls, and policies, all in a single blueprint.
Environment creation streamlining
Azure Blueprints allows you to organize blueprints into different subscriptions to generate a single conforming bundle. Managing and tracking can be done from a central location to get rapid updates.
Enable compliant development
Azure blueprints may build a speedier compliance-based application using the self-service architecture, as well as make it easier to organize the compliance application according to production requirements.
Lock foundational resources
Azure Blueprints can help you minimize unpleasant alterations and misconfigurations, including those made by subscription owners. Resource-looking options in the Azure blueprint can restrict access to shared infrastructure across subscriptions.
Landing zone creation while migrating to Azure
Without the need for external architects, you may speed up the migration process by simply planning the landing zone.
FAQs
Is the Azure blueprint free?
Azure Blueprints and other Azure services are available for free to help manage Azure services. Certain functions require the user to have a paid subscription.
What's the difference between Azure Blueprints and Azure Policies?
Azure Policies primarily serve as an access control mechanism, providing default permissions (allow or deny) for new and existing resources to which the policy applies.
Azure Blueprints, on the other hand, are packages that define and enforce certain rules and requirements for Azure service deployment, as well as security and design principles. These packages are designed to promote consistent and compliant resource implementation in Azure environments.
What's the difference between Azure landing zones and Azure Blueprints?
An Azure Landing Zone is linked to the core components of an organization's Azure setup. It is simply a collection of resources that serve as the foundation for an organization's Azure configuration.
Azure Blueprints, on the other hand, are templates for standardizing configurations and settings across several Azure resources. They can be used to provide this uniform configuration among numerous partners or projects.